Antibiotics are developed and synthesized to act specifically on bacterial cell walls and RNA to inhibit protein synthesis. Human cells do not need peptidoglycan.
Select the right antibiotics for your cells.
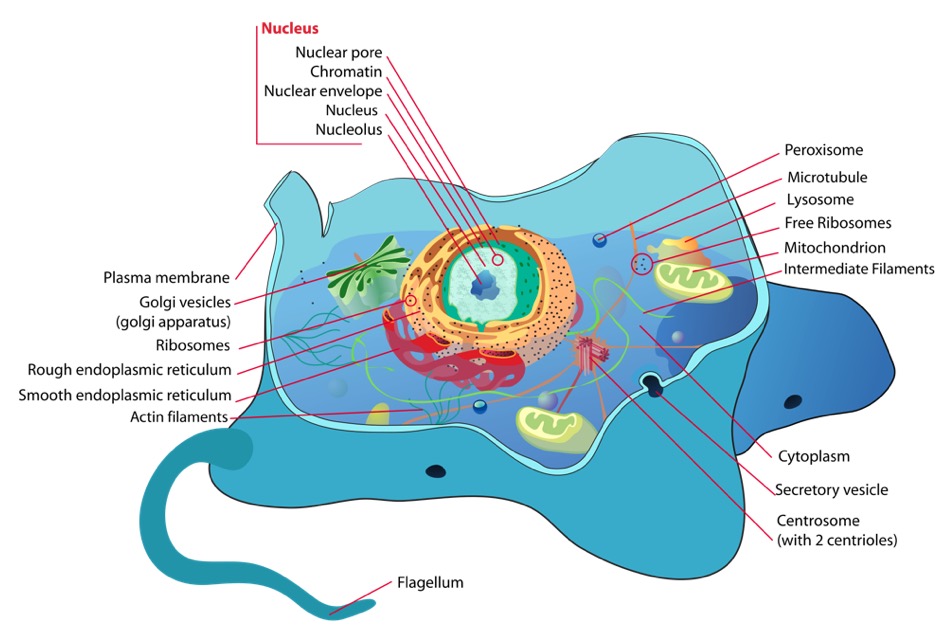
. Mycoplasma are the smallest free-living 03 µM prokaryotes observed as filamentous or coccal forms under scanning electron microscope. Antibiotic peptides from higher eukaryotes. The six major targets of antibiotics include.
Antibiotics work by interfering with the bacterial cell wall to prevent growth and replication of the bacteria. Depending on these effects an antibiotic is said to be bactericidal or bacteriostatic. A bactericidal antibiotic kills the bacteria while the bacteriostatic antibiotics stops bacterial growth but does not kill the cells.
The introduction of antibiotics into medicine revolutionised the way infectious diseases were treated. This class of antibiotics interferes with the bacterial cells ability to copy its DNA genetic material. Antibiotics deeply influence cell metabolism.
Something that must be done before a cell can divide and multiply. These effects are the consequence of the. A group of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones target that enzyme which blocks DNA replication and thus a bacteria can no longer reproduce.
Gene-encoded antibiotic peptides are increasingly being recognized as effector molecules of host defense in plants and animals. They kill prokaryotic cells while leaving eukaryotic cells unharmed by targeting the differences between the two cell types. Although human cells also make proteins the protein-making cellular machinery is different in eukaryotic cells so it is not harmed by Tetracyclines.
Antibiotics recognize the mitochondria and chloroplasts as eukaryotic and dont attack those cells. Antibiotics are either bactericidal they kill the bacteria or bacteriostatic they keep the bacteria from. All antibiotics target the cell wall.
Drugs inhibit ribosome function either by interfering in messenger RNA translation or by blocking the formation of peptide bonds at the peptidyl transferase centre. Similar findings were obtained when using aminoglycosides such as streptomycin or gentamicin Fischer et al 1975 Cooper at al 1990. Though certain antibiotics that do affect eukaryotic cells have been exploited in cell culture systems and other research applications to better understand mammalian cell biology.
Bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotics. They either prevent the reproduction of bacteria or they kill the bacteria for example by stopping the mechanism responsible for building their cell walls. Some antibiotics prevent bacteria from producing a cell wall which eukaryotic cells lack Prokaryotes have different DNA which is how the antibiotics target bacteria rather than our cells.
There are two main ways in which antibiotics target bacteria. Determine suitable antibiotic concentration for your cells. Studies of antimicrobial peptides are providing new insights into the dynamic interactions between microbes and their hosts and are generating new paradigms for the.
Answer 1 of 36. Why are antibiotics important. Human cells do not have cell walls but many types of bacteria do and so antibiotics can target bacteria without harming human cells.
Human cells do not make or need peptidoglycan. Penicillin one of the first antibiotics to be used widely. Antibiotics do harm both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Though certain antibiotics that do affect eukaryotic cells have been exploited in cell culture systems and other research applications to better understand mammalian cell biology or to control certain cellular functions. From the 1970s to the 90s numerous reports presented evidence of the antiproliferative effects of beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillin on cultured eukaryotic cells Neftel et al 1987. Bacteria produce a cell wall that is composed partly of a macromolecule called peptidoglycan made up of amino sugars and peptides.
They kill eukaryotic cells while leaving prokaryotic cells unharmed by targeting the differences between the two cell types. As it turns out bacteria use some enzymes that are not found in eukaryotic cells such as DNA gyrase. Penicillin one of the first antibiotics to be used widely prevents the final cross-linking step or transpeptidation in assembly of this.
The last mechanism of action involves targeting a specific compound - folate. As a matter of fact penicillin is actually produced by a fungus. Most importantly to be safe as well as effective against microbes these compounds must target mechanisms specific to prokaryotic cells without affecting eukaryotic function.
This either kills the bacterium or slows down bacterial growth. Antibiotic-induced cell death has been associated with the formation of double-stranded DNA breaks following treatment with DNA gyrase inhibitors 4 with the arrest of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis following treatment with rifamycins 5 with cell envelope damage and loss of structural integrity following treatment with cell-wall synthesis inhibitors 6 and with cellular energetics. Antibiotics arent effective against eukaryotic cells because they dont chemically bind with their cell walls or rna.
Geneticin G418 Sulfate an aminoglycoside antibiotic is an elongation inhibitor of 80 S ribosomes that blocks polypeptide synthesis by inhibiting the elongation step in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. How do antibiotics work. Mycoplasma contamination is cryptic and extremely challenging to handle.
The ribosome is a major bacterial target for antibiotics.

Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Differences Examples
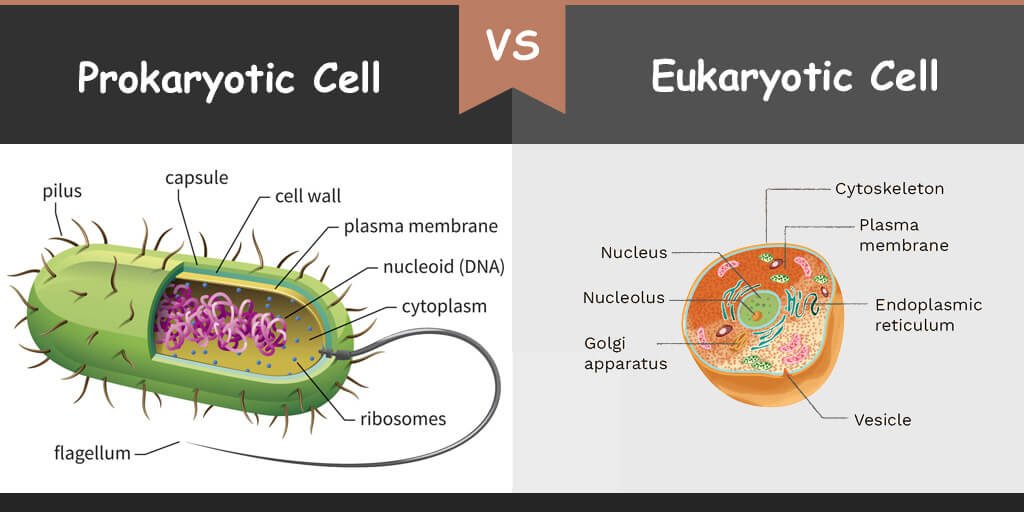
Prokaryotic Cells Vs Eukaryotic Cells Diffzi

Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet For Review Or Assessment Cells Worksheet Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes

Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Differences Examples
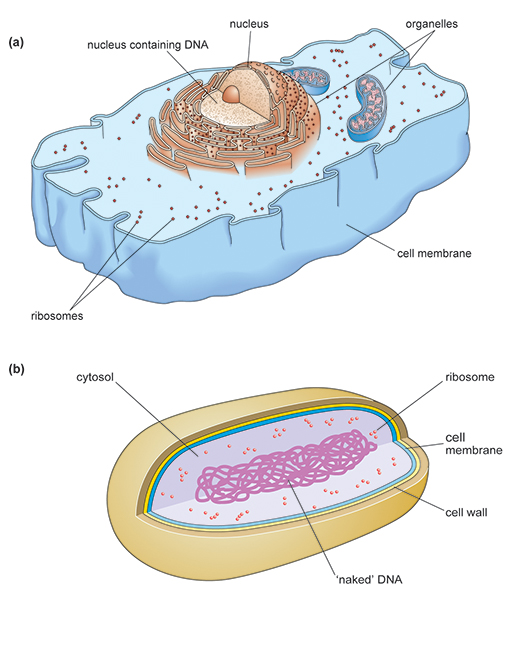
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance Openlearn Open University

Antibiotic Resistance Guided Reading Pdf Digital Versions Applied Science Guided Reading Middle School Science

Cell Types Eukaryotic Versus Prokaryotic Concise Medical Knowledge
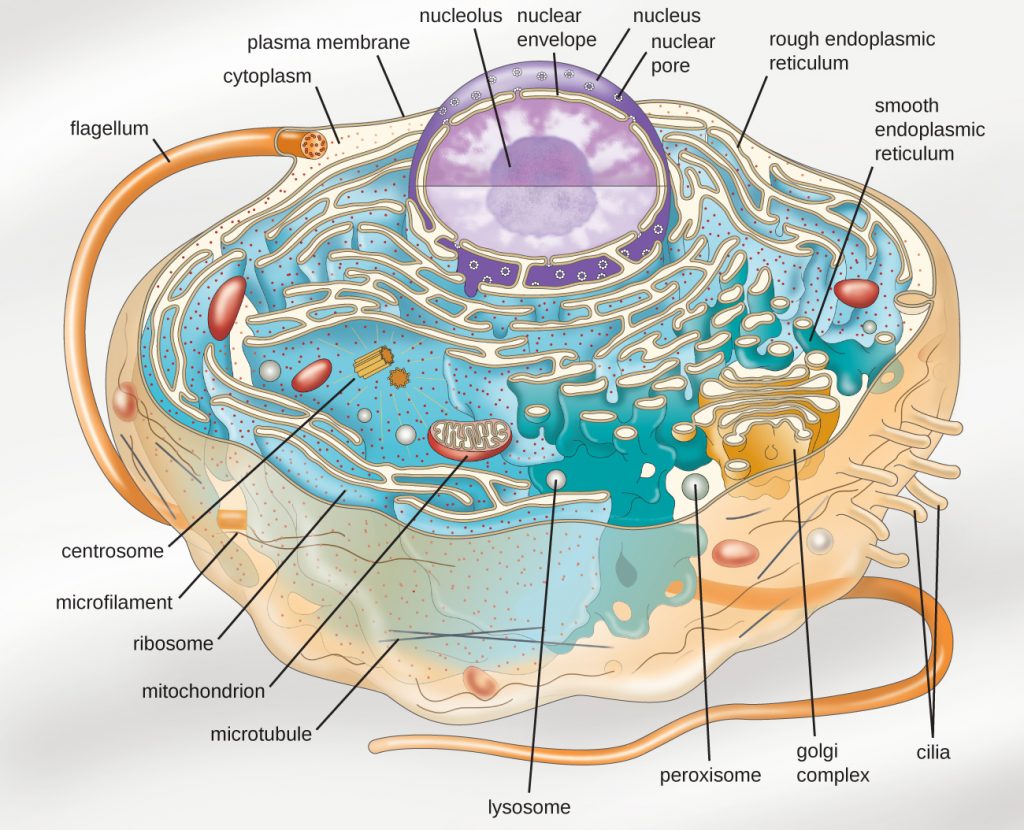
3 4 Unique Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology Canadian Edition


0 Comments